Keeping in mind the end goal to comprehend the distinctive kinds of polypropylene, one needs to dive in and comprehend thermoplastics classes with an alternate perspective. Thermoplastics are arranged into two gatherings: product thermoplastics, this gathering covers the significant plastics, for example, polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene and polyvinyl chloride. They have additionally sub-divisions, for example, PP-homo-polymers and Co-polymers, PVC-Rigid and Plasticized, PE-High thickness, low thickness and direct low thickness. Designing thermoplastics is the second thermoplastics gathering and items in this class are identified with electrical and mechanical building applications. Utilizing these plastics may supplant different materials like metals and load-bearing parts. These incorporate polysulfone, nylons, polycarbonates, acetal and ABS terpolymers.
Notwithstanding, thermoplastics are described by softening after warming and solidifying by cooling which is leverage in handling strategies, for example, expulsion or infusion shaping where disposed of materials can be reused. Polypropylene is found in three stereo particular setups: isotactic, methyl bunches on one side of polymer spine, syndiotactic, methyl bunches interchange on the two sides and atactic, unpredictable game plan of methyl assemble. Liquefying purpose of splendidly isotactic PP is 171°C, yet syndiotactic PP (30% crystallinity) has a softening purpose of 130°C. Polypropylene is alluring to petrochemical organizations on account of its extraordinary properties. For example, polypropylene is semi-unbending, translucent, a great compound obstruction, extreme, a great weariness opposition and a decent warmth opposition. In addition, PP has high softening or glass-progress guide, high opposition toward flexing pressure, low water retention, great electrical obstruction, a lightweight, dimensional security, high effect quality and a non-poisonous quality property. PP is stiffer than HDPE and biaxial introduction of PP brings about movies and compartments with predominant optical and obstruction properties. Table 1 demonstrates properties of isotactic homo-polypropylene for instance.
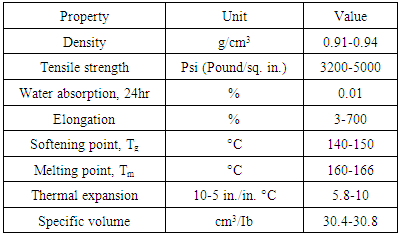
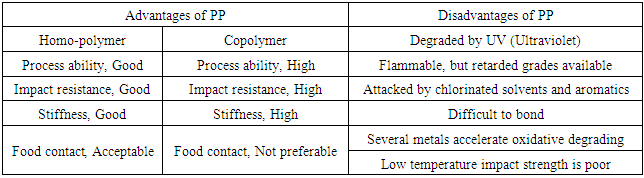
Table 1. Properties of Isotactic Homo-polypropylene
There are three distinct kinds of polypropylene. To start with, polypropylene containing just propylene monomer in a semi-crystalline strong shape; which is known as a homo-polymer PP (HPP). Second, polypropylene containing ethylene as a co-monomer in the PP chains at levels in the scope of 1-8% and this is alluded to as an irregular copolymer (RCP). Third, HPP containing a co-blended RCP stage that has an ethylene substance of 45-65% is alluded to as an effect copolymer (ICP). When all is said in done, polymers comprising of indistinguishable monomers are called homo-polymers where polymeric mixes with in excess of one kind of monomer in their chains are known as co-polymers.
Homo-polymer PP (HPP) is the most broadly utilized polypropylene material in industry. HPP is a two-stage framework contains both crystalline and non-crystalline locales. The non-crystalline (nebulous) districts have both isotactic PP and atactic PP. The isotactic PP in the undefined locales is crystallizable and takes shape gradually after some time. At the end of the day, HPP comprises of just a single propylene unit along the chain with for the most part isotactic propylene units and that give us a crystalline structure to the polymer. Consequently, HPP shows an abnormal state of firmness at room temperature and a high dissolving point yet bring down straightforwardness and additionally lessened effect quality. Irregular copolymers (RCP) are ethylene/propylene copolymers that are created in a solitary reactor by copolymerizing propylene and little measures of ethylene (generally 7% or lower). Ethylene upsets the customary structure of polypropylene and results in a diminishment of crystalline consistency in the polymer. The connection amongst ethylene and crystalline thickness is conversely relative which implies that as the ethylene content builds the crystalline thickness bit by bit diminishes and bringing about achieving lower liquefying point. Co-polymers, for the most part, have marginally better effect properties, diminished softening point and upgraded adaptability. Effect copolymers (ICP) are physical blends of HPP and RCP with a general ethylene substance around 6-15% weight. Effect polymers are ideal at low temperatures with higher effect obstruction. The RCP part of the blend is intended to have ethylene substance in the request of 40-65% ethylene and it is known as the elastic stage. The elastic-like fortification extraordinarily enhances affect quality especially at low temperatures (beneath − 20°C). Be that as it may, solidness is held bringing about phenomenal firmness/affect adjust. ICP item and in addition the effect opposition shifts as for size, shape and dissemination of the elastic particles. A correlation between homo-polymers and copolymers in their focal points and inconveniences of PP, when all is said in done, is shown in Table 2.
| Advantages of PP | Disadvantage of PP | |
| Homo-polymer | Copolymer | Degraded by UV (Ultraviolet) |
| Process ability, good | Process ability, high | Flammable, but retarded grades available |
| Impact resistance, good | Impact resistance, high | Attacked by chlorinated solvents and aromatics |
| Stiffness, good | Stiffness, high | Difficult to bond |
| Food contact, acceptable | Food contact, not preferable | Several metals accelerate oxidative degrading |
| Low temperature impact strength is poor | ||
Table 2. Advantages and Disadvantages of Polypropylene
The accompanying is the surmised piece of the pie for PP composes: homo-polymer (HPP) 65-75%, affect copolymer (ICP) 20-30% and irregular copolymer (RCP) 5-10%. By and large, extraordinary PP grades are accessible rely upon the required application. Business grades are accessible in an assortment of atomic weight circulations, and co-monomer writes and in addition substance and added substances. Improved physical properties enable polypropylene to be the center material in most requesting applications, for example, films, filaments, tapes, sheets, thermoforming, infusions, and blow forming. Some mechanical and warm properties of business polypropylene in addition to an examination of warm conductivity and recoverable vitality substance of various plastics are appeared in Table 3 and Table 4, individually.
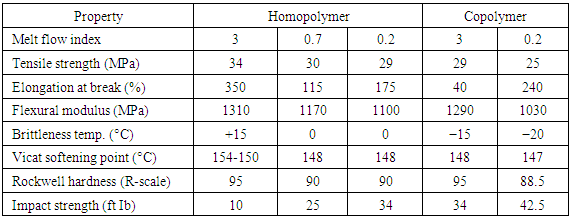
Table 3. Mechanical & Thermal Properties of Polypropylene
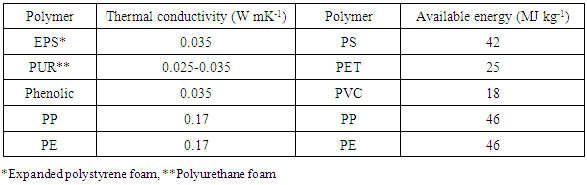
Table 4. Thermal Conductivity & Recoverable Energy of Plastics
Reusing of polymers causes exhaustion in their mechanical and optical properties. Optical qualities are critical for sustenance bundling applications. A business polypropylene review called semi-crystalline isotactic polypropylene (iPP) was contemplated in a past work to guarantee a reasonable darkness after reusing. Semi-crystalline iPP structures describe with a few precious stone alterations including monoclinic (), trigonal (β) and orthorhombic (γ) frames. Optical straightforwardness in semi-crystalline polymers relies upon crystallinity, morphology and surface properties. The lower the straightforwardness is the more dimness we get. Subsequently, lessened crystallinity expands the lucidity of the item. iPP polymers are expelled, reused, a few times and cooled upon expulsion to see the impact of reusing on murkiness. It is discovered that obscurity diminishes on expanding reusing steps and cooling rate. Nonetheless, expanding the measure of stage and expanding their normal size of the spherulites builds mistiness. β-alteration of isotactic polypropylene (β-iPP) is another business review with one of a kind highlights. For instance, sturdiness and effect quality of β-iPP altogether surpass those of – iPP. The advancement of β-stage is finished by crystallization in a temperature angle or in a stressed dissolve. However, β-change can’t substitute or drop the utilization of – alteration since each review has its own prevalent properties. Results demonstrated that iPP grades have fantastic mechanical properties and suitable optical qualities. Ordinary properties for different semi-crystalline saps and thermoplastic composites with glass filaments and stage progress temperatures for regular semi-crystalline thermoplastic pitches are outlined in Tables 5 and 6, individually.
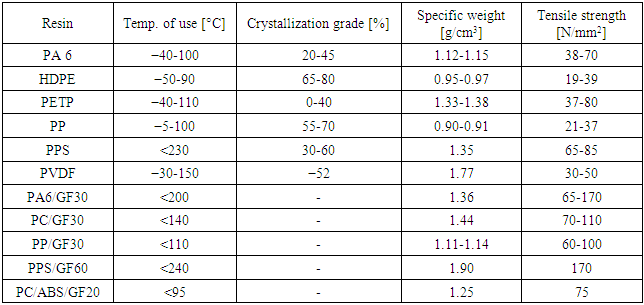
Table 5. Typical Properties for Various Semi-crystalline Resins and Thermoplastic Composites with Glass Fibers
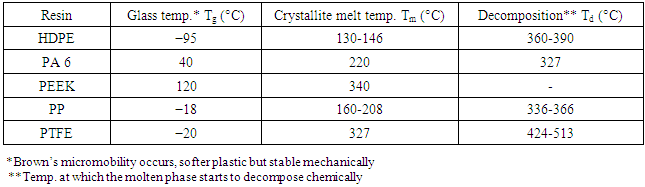
Table 6. Phase-transition Temperatures for Semi-crystalline Resins
Low temperature fragility is a negative foundation for PP polymers in specific applications. A promising procedure demonstrated that prevalent adjust of effect quality and modulus is conceivable by mixing PP with different elastomers, for example, ethylene-propylene irregular copolymer (EPR), styrene-butadiene-styrene square copolymer (SBS), ethylene-propylene-diene terpolymer (EPDM) and isoprene-styrene di-square copolymer (ISR-A). For instance, a mix of 80/20 and 70/30 of PP/ISR-A have a high effect quality of 83 and 100 J/m, with flexural modulus of 1280 and 1070 MPa, separately, contrasted with those consequences of PP (32 J/m, 1530 MPa).