Material cost of injection molding
The material cost is dictated by the heaviness of material that is required and the unit cost of that material. The heaviness of material is obviously a consequence of the part volume and material thickness; be that as it may, the part’s greatest divider thickness can likewise assume a part. The heaviness of material that is required incorporates the material that fills the channels of the shape. The measure of those channels, and thus the measure of material, is to a great extent dictated by the thickness of the part.
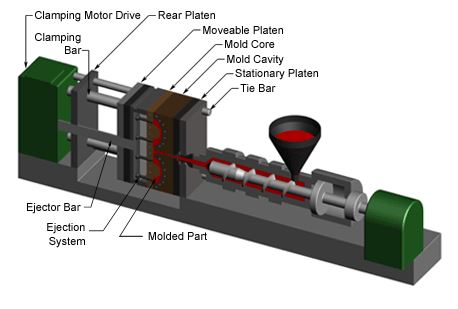
Production cost of injection molding
The creation cost is basically ascertained from the hourly rate and the process duration. The hourly rate is relative to the measure of the infusion shaping machine being utilized, so it is essential to see how the part configuration influences machine determination. Injection molding machines are regularly alluded to by the tonnage of the cinching power they give. The required bracing power is controlled by the anticipated zone of the part and the weight with which the material is infused. In this manner, a bigger part will require a bigger clipping power, and henceforth a more costly machine. Likewise, certain materials that require high infusion weights may require higher tonnage machines. The measure of the part should likewise agree to other machine determinations, for example, clip stroke, platen size, and shot limit.
The process duration can be separated into the infusion time, cooling time, and resetting time. By lessening any of these circumstances, the generation cost will be brought down. The infusion time can be diminished by decreasing the most extreme divider thickness of the part and the part volume. The cooling time is likewise diminished for bring down divider thicknesses, as they require less time to cool completely through. A few thermodynamic properties of the material additionally influence the cooling time. In conclusion, the resetting time relies upon the machine measure and the part estimate. A bigger part will require bigger movements from the machine to open, close, and discharge the part, and a bigger machine requires more opportunity to play out these tasks.
Tooling cost of injection molding
The tooling cost has two primary parts – the shape base and the machining of the cavities. The cost of the form base is fundamentally controlled by the span of the part’s envelope. A bigger part requires a bigger, more costly, shape base. The cost of machining the depressions is influenced by almost every part of the part’s geometry. The essential cost driver is the span of the hole that must be machined, estimated by the anticipated region of the cavity (equivalent to the anticipated region of the part and anticipated gaps) and its profundity. Whatever other components that will require extra machining time will add to the cost, including the element tally, separating surface, side-centers, lifters, unscrewing gadgets, resistance, and surface unpleasantness.
The amount of parts additionally impacts the tooling cost. A bigger creation amount will require a higher class form that won’t wear as fast. The more grounded shape material outcomes in a higher form base cost and additionally machining time.
One last thought is the quantity of side-activity headings, which can in a roundabout way influence the cost. The extra cost for side-centers is controlled by what number of are utilized. Nonetheless, the quantity of bearings can limit the quantity of holes that can be incorporated into the shape. For instance, the shape for a section which requires 3 side-activity headings can just contain 2 cavities. There is no immediate cost included, however it is conceivable that the utilization of more depressions could give encourage funds.